5 Most Serious Risk Associated with Bed Side Rails You Must Know
📋 KEY TAKEAWAYS
| Risk | Description | Affected Population |
|---|---|---|
| Entrapment | Head, neck, or chest caught between rails or mattress | Elderly, confused patients, small-framed adults |
| Injury Severity | Can cause suffocation, strangulation, death | Highest risk in unmonitored environments |
| FDA Data | Over 800 entrapment incidents reported | Majority involving adults over 60 |
| Risk Zones | 7 critical zones identified by FDA | Most dangerous: gaps between rails and mattress |
| Prevention | Proper sizing, gap fillers, alternative devices | Regular risk assessments essential |
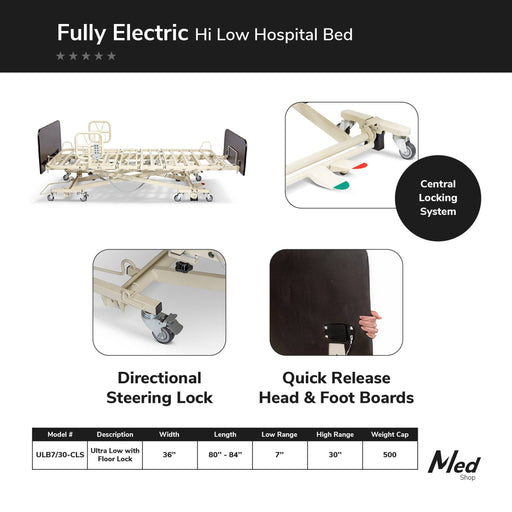
Safest Rails Option: Costcare BPR300 Composite Swing Down Rails – Designed to FDA safety standards
Best Complete Solution: Icare Adjustable Electric Home Hospital Bed IC333 – Integrated safety system
For Enhanced Safety: Icare Homecare Bed Padded Side Rail Covers – Reduces entrapment risk
What is considered to be the most serious risk associated with bed side rails? Without question, entrapment is the gravest danger, accounting for numerous injuries and fatalities each year. This life-threatening situation occurs when a person becomes caught, trapped, or entangled between the bed's side rail, mattress, or bed frame.
For anyone caring for elderly or vulnerable individuals using hospital beds or beds with safety rails, understanding these risks is essential. Despite being designed to increase safety, improperly fitted or used bed rails can create dangerous hazards that have resulted in hundreds of documented deaths and thousands of injuries.
This comprehensive guide examines the five critical facts about bed rail entrapment, FDA safety guidelines, prevention strategies, and safer alternatives including specialized hospital bed mattresses and properly designed rail systems for both standard and bariatric hospital beds.
1. Understanding Entrapment: The Primary Danger of Bed Side Rails
Entrapment occurs when a person's body or part of their body becomes caught between the bed rail and another part of the bed, typically the mattress or bed frame. This risk is particularly severe because of its potential fatal consequences.
The Mechanics of Entrapment
-
Head and Neck Entrapment: The most lethal form occurs when a person's head becomes caught in a gap, leading to potential strangulation or suffocation.
-
Chest Compression: When the chest becomes trapped and compressed, breathing can be restricted, resulting in asphyxiation.
-
Limb Entrapment: While less immediately life-threatening, limb entrapment can cause serious injuries, circulation issues, and nerve damage.
-
Full-Body Entrapment: In some cases, patients attempting to exit the bed become trapped between the rail and mattress in a way that prevents them from returning to a safe position.
High-Risk Populations
Those most vulnerable to entrapment risks include:
- Elderly individuals with reduced cognitive awareness and physical strength
- Patients with conditions like dementia, Alzheimer's, or confusion
- Small-framed adults who can more easily slip into gaps
- People with limited mobility who may struggle to free themselves
- Agitated or restless individuals who move frequently in bed
According to FDA data, over 80% of reported entrapment incidents involve adults over 60 years of age. This underscores the particular danger to elderly individuals using beds with side rails.
To minimize these risks, specialized options like the Costcare BPR300 Composite Swing Down Rails are designed with safety gaps that meet FDA guidelines.
2. FDA Zones of Entrapment: Identifying Critical Risk Areas
The FDA has identified seven specific zones around hospital beds and side rails where entrapment is most likely to occur. Understanding these zones is critical for proper risk assessment and prevention.
| Zone | Location | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Zone 1 | Within the rail itself | Moderate |
| Zone 2 | Between rail supports | High |
| Zone 3 | Between rail and mattress | Very High |
| Zone 4 | Between rail and footboard | High |
| Zone 5 | Between split bed rails | Very High |
| Zone 6 | Between rail end and headboard | High |
| Zone 7 | Between headboard/footboard and mattress end | Moderate |
Zone 3: The Most Dangerous Area
Zone 3, the space between the rail and the mattress, is considered the most critical entrapment area. This danger zone is where the majority of fatal incidents occur, as it can trap a person's neck or chest, leading to strangulation or suffocation.
The FDA has established detailed dimensional guidelines for these zones:
-
Width requirements: Gaps in Zones 1-4 should be less than 4.75 inches (to prevent head entrapment)
-
Mattress compression: Zone 3 must account for mattress compression when a person leans against the rail
-
Rail height: Rails must extend at least 8.66 inches above the mattress to prevent patients from rolling over them
Modern, safety-focused rails like the Icare Occupation Therapist U-Assist Side Rail are designed to meet or exceed these specifications, significantly reducing entrapment risks.
3. FDA Data and Incident Reports: The Scope of the Problem
The statistics on bed rail entrapment reveal the severity of this safety issue and the urgent need for awareness and preventive measures.
Statistical Overview
-
FDA reports: Over 800 entrapment incidents reported, with approximately 480 resulting in death
-
Timeframe data: Over a 32-year monitoring period (1985-2017), averaging 15 deaths per year
-
Underreporting: Experts believe actual numbers are significantly higher due to inconsistent reporting
-
Location distribution: 50% of incidents occur in skilled nursing facilities, 25% in hospitals, and 25% in private homes
-
Age demographics: 65% of victims are over 75 years old
Severity of Outcomes
The consequences of entrapment incidents are severe:
- Fatal outcomes: Approximately 60% of reported entrapment incidents result in death
- Serious injuries: Non-fatal incidents frequently cause severe injuries including fractures, dislocations, and tissue damage
- Psychological trauma: Survivors often experience significant psychological distress and fear
- Long-term complications: Survivors may develop complications from prolonged compression or restricted blood flow
These statistics highlight why entrapment is considered the most serious risk associated with bed side rails, outweighing other concerns such as falls or rail-related injuries.
To address these concerns, beds like the Icare Adjustable Electric Home Hospital Bed IC333 incorporate modern safety design principles to minimize entrapment zones while still providing necessary support.
4. Contributing Factors That Increase Entrapment Risk
Several critical factors can dramatically increase the risk of entrapment beyond the inherent dangers of the bed rail design itself.
Mattress and Bed Compatibility Issues
-
Improper mattress fit: Mattresses too small for the bed frame create dangerous gaps
-
Mattress compression: Over time, mattresses compress and create larger gaps with rails
-
Mattress replacement: Using replacement mattresses not designed for the specific bed
-
Bariatric adaptations: Standard rails used with wider bariatric hospital beds create hazardous spaces
Patient-Specific Risk Factors
-
Cognitive impairment: Confusion leads to attempts to exit the bed in unsafe ways
-
Agitation and restlessness: Increased movement raises entrapment likelihood
-
Medication effects: Sedatives or sleep aids may reduce awareness of entrapment
-
Physical limitations: Weakness prevents self-rescue when entrapment occurs
-
Size and weight: Very thin patients can slip into smaller gaps
Environmental and Care Factors
-
Inadequate monitoring: Reduced supervision increases risk, especially at night
-
Improper rail use: Using rails as restraints rather than mobility aids
-
Staff training gaps: Caregivers unaware of proper assessment and prevention
-
Maintenance issues: Worn mechanisms creating larger gaps or loose components
-
Multiple bed adjustments: Frequent position changes creating temporary gaps
The combination of these factors explains why entrapment continues to occur despite safety guidelines. For optimal safety, it's crucial to use properly sized hospital bed mattresses designed specifically for the bed frame and side rail configuration.
5. Prevention Strategies and Safer Alternatives
Preventing entrapment requires a multifaceted approach combining proper equipment, regular assessment, and appropriate alternatives.
Equipment-Based Prevention
-
Compliant bed systems: Use hospital beds that meet current FDA safety guidelines
-
Gap fillers: Install products designed to fill dangerous gaps between rails and mattresses
-
Rail covers: Products like Icare Homecare Bed Padded Side Rail Covers reduce entrapment spaces
-
Proper mattress sizing: Ensure mattresses properly fit the bed frame without gaps
-
Alternative rail designs: Consider safer designs like:
- Half-rails instead of full-length rails
- Transfer poles and grab bars
- Concave rails that eliminate gaps
Assessment and Protocols
-
Individual risk assessment: Evaluate each patient's specific entrapment risk
-
Regular gap measurement: Check all seven entrapment zones using FDA measurement tools
-
Documentation: Maintain records of assessments and interventions
-
Routine inspections: Regularly check for wear, damage, or shifting components
-
Policy development: Establish clear protocols for rail use and alternatives
Safer Alternatives to Traditional Side Rails
| Alternative | Benefits | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Roll Guards | Soft barriers without rigid components | Fall prevention without entrapment risk |
| Concave Mattresses | Center depression keeps patient positioned | Mobile patients who roll in bed |
| Bed Alarms | Alert caregivers when patient attempts to exit | Patients requiring monitoring without restraint |
| Floor Mats | Cushion falls without creating entrapment | Patients who may roll out of bed |
| Ultra-Low Beds | Minimal fall height without side rails | High fall risk patients who don't need rails |
For many situations, the safest approach is a properly designed bed system that minimizes the need for traditional side rails while still providing necessary support and safety.
Legal and Regulatory Framework Addressing Entrapment
The serious nature of entrapment risks has prompted significant regulatory oversight and legal consequences for manufacturers, facilities, and caregivers.
FDA Guidelines and Regulations
-
Hospital Bed System Dimensional and Assessment Guidance: Published in 2006, provides specific measurements for entrapment zones
-
Mandatory reporting: Facilities must report entrapment incidents to the FDA
-
Bed rail safety alerts: The FDA has issued multiple safety communications
-
Classification: Most bed rails are considered Class I or Class II medical devices
-
Inspection authority: FDA can inspect facilities for compliance with safety standards
Facility and Caregiver Responsibilities
-
Assessment requirements: Facilities must assess entrapment risk for each patient
-
Documentation: Must maintain records of assessments and interventions
-
Patient rights: Must respect patient autonomy while providing adequate protection
-
Staff training: Required to train caregivers on entrapment risks and prevention
-
Equipment maintenance: Responsible for regular inspection and maintenance
Legal Consequences of Entrapment Incidents
The legal ramifications of entrapment incidents can be severe:
- Wrongful death lawsuits: Families can sue when deaths occur due to entrapment
- Personal injury claims: Survivors or their representatives can seek damages
- Regulatory penalties: Facilities can face fines and sanctions for non-compliance
- Criminal charges: In cases of gross negligence, criminal charges may be possible
- Licensure consequences: Healthcare providers may face professional discipline
These legal and regulatory frameworks underscore the serious nature of entrapment risks and the responsibility of all parties to address them proactively.
Alternative designs like the Emerald Q Assist Bar Medical Bed Assist Rail provide positioning support with significantly reduced entrapment risk compared to traditional side rails.
Risk Mitigation for Different Care Settings
Addressing entrapment risks requires different approaches based on the care setting, as each environment presents unique challenges and resources.
Hospital Setting Risk Mitigation
-
Standardized assessment: Implement formal entrapment risk evaluation on admission
-
Equipment selection: Use only compliant beds and accessories
-
Regular monitoring: Increase frequency of patient checks
-
Staff training: Provide specific education on entrapment zones and prevention
-
Alternatives protocol: Develop a decision tree for bed rail alternatives
Long-Term Care Facility Approaches
-
Resident-specific plans: Develop individualized rail use protocols
-
Environmental modifications: Create safer room environments to reduce rail need
-
Regular reassessment: Evaluate entrapment risk as resident condition changes
-
Family education: Involve families in understanding risks and alternatives
-
Equipment tracking: Monitor rail compatibility with specific beds and mattresses
Home Care Setting Strategies
-
Home assessment: Evaluate the specific bed setup for entrapment risks
-
Caregiver education: Train family members on proper rail use and alternatives
-
Simplified monitoring: Implement easy-to-use check systems for non-professionals
-
Proper equipment: Select home medical beds designed for safety, like the Icare Adjustable Electric Home Hospital Bed IC333
-
Regular professional review: Schedule periodic reassessment by healthcare providers
By tailoring entrapment prevention strategies to the specific care environment, the risks can be significantly reduced while still meeting patient needs for support and safety.
Creating a Comprehensive Entrapment Prevention Plan
Effective prevention of entrapment requires a structured, comprehensive approach that addresses all aspects of the risk.
Assessment Components
-
Patient/resident evaluation: Assess cognitive status, mobility, behavior
-
Equipment inspection: Check all seven entrapment zones with proper tools
-
Compatibility verification: Ensure bed, mattress, and rails are designed to work together
-
Environmental review: Evaluate room layout and additional risk factors
-
Monitoring capacity: Assess ability to provide appropriate supervision
Implementation Steps
-
Decision protocol: Use assessment results to determine appropriate interventions
-
Documentation system: Record all assessments, decisions, and interventions
-
Staff training program: Educate all caregivers on risks and proper procedures
-
Equipment maintenance schedule: Set regular inspection and maintenance timetables
-
Family involvement: Include family members in prevention planning
Specialized Considerations for Bariatric Patients
Bariatric hospital beds present unique entrapment challenges requiring specific attention:
- Wider dimensions: Increased distances create larger potential entrapment zones
- Specialized mattresses: Require bariatric-specific mattresses to prevent gaps
- Weight factors: Increased compression of surfaces can create temporary gaps
- Modified rails: Need rails specifically designed for bariatric applications
- Reinforced components: Must ensure all parts maintain integrity under increased weight
For bariatric applications, beds like the Costcare Bariatric Adjustable Hospital Bed B359 are specifically engineered to address these unique challenges.
Our Top Recommendation for Entrapment Prevention
After analyzing all the factors contributing to entrapment risk and the available solutions, the Icare Adjustable Electric Home Hospital Bed - IC333 emerges as our top recommendation for minimizing entrapment risks while providing necessary support.
This premium hospital bed achieves the ideal balance of:
- FDA-compliant design: Engineered to minimize entrapment zones
- Integrated safety system: Coordinated bed, rails, and mattress design
- Adjustable features: Reduces need for rails through height adjustment
- Quality construction: Maintains proper specifications over time
- Compatible accessories: Works with entrapment-reducing add-ons like rail covers
When combined with proper assessment, monitoring, and caregiver education, this system provides the most comprehensive approach to preventing the serious risk of entrapment associated with bed side rails.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is entrapment in bed rails and why is it dangerous?
Entrapment occurs when a person becomes caught between the bed rail and mattress. It's extremely dangerous because it can cause suffocation, strangulation, or severe bodily injury when a person's head, neck, or chest gets trapped.
Which patient groups are at highest risk for bed rail entrapment?
Elderly patients with confusion or dementia, small-framed adults, those with limited mobility, and patients taking sedative medications face the highest risks for entrapment incidents.
What are the FDA's guidelines for preventing bed rail entrapment?
FDA guidelines specify maximum gap sizes (less than 4.75 inches for most areas), requirements for seven different zones around the bed, and proper compatibility between beds, mattresses, and rails.
Can entrapment risks be eliminated while still using bed rails?
While risks can be significantly reduced through proper assessment, compliant equipment, gap fillers, and monitoring, they cannot be completely eliminated when using traditional side rails.
What alternatives exist to traditional bed rails that reduce entrapment risk?
Safer alternatives include ultra-low beds, floor mats, roll guards, concave mattresses, bed alarms, and specialized mobility aids like transfer poles and assist bars.
Is Medicare coverage affected by the type of bed rail safety equipment used?
Medicare typically covers medically necessary equipment, including compliant bed rails, when prescribed by a physician. Coverage may be denied for non-compliant or outdated equipment that presents known safety hazards.